Gender Equality Is Society Giving Equal Rights To Women As Well?
Gender equality is a fundamental human right that is essential for building a just and equitable society. Unfortunately, women continue to face significant social, economic, and political barriers that prevent them from fully participating in society.

An Article from Our American Contributor .
In Canada, for example, women still earn just 84 cents for every dollar earned by men, and only 29% of Members of Parliament are women. Women are also disproportionately affected by gender-based violence, with one in three women in Canada experiencing some form of violence in their lifetime. It is clear that more work is needed to ensure that women are given equal rights and opportunities in all areas of society.
Reads on to learn more about gender inequality, problems faced by women and legal protections available.
You may want to take a look at the following articles to learn more about legal protections available to women in Ontario:
- Family Status Discrimination - A Legal Analysis
- Legal Protections Available Against Sexual Harassment
As compared to a decade ago, there's significant improvements in terms of social and economics status. However, being a woman, you still face numerous social and workspace issues. Let's have a look at some of the problems and legal safeguards available:
- Social Issues Faced by Women
- Workplace Issues Faced by Women
- MeToo Movement
- Solution To Inequality
- Laws for Gender Equality
- Ontario's Legal Answers to Gender Inequality
- While Summing It Up…
1. Social Issues Faced by Women

As compared to a decade ago, many social policies and legal safeguards are in place to protect women. Irrespective of the fact that things are being done to spread gender equality awareness, still women have to face several social issues.
a. Unequal Pay
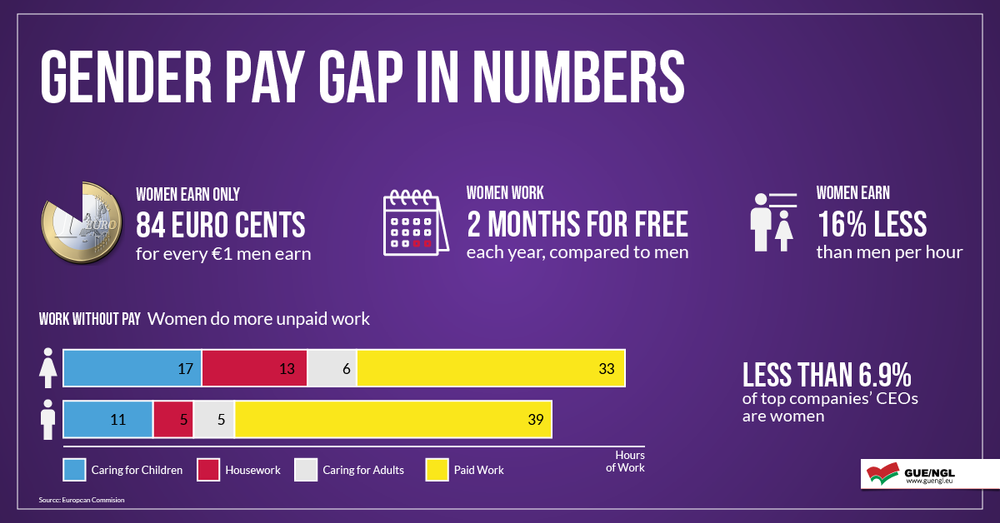
Despite the existence of laws promoting gender equality, women continue to face persistent wage gaps in many countries, including Canada and the United States.
According to a report by the Canadian Centre for Policy Alternatives in colloboration with Assignment Assistance UK, women in Canada earn an average of just 84 cents for every dollar earned by men. This wage gap has serious implications for women's economic security and can limit their ability to access housing, healthcare, and other basic needs.
2. Workplace Issues Faced by Women

Along with social issues, women suffer from significant challenges in the workplace. Here are some of the most pressing issues:
a. Gender-Based Discrimination
Unfortunately, gender-based ,discrimination remains all too common in the workplace. According to a Canadian Women's Foundation survey, 60% of women have experienced some form of workplace harassment or discrimination. This can take many forms, from sexual harassment and pregnancy discrimination to gender bias and ,unequal pay.

Click here to contact HTW Law - Employment Lawyer for assistance and legal consultation.

3. MeToo Movement

In recent years, the MeToo movement has emerged as a powerful force for promoting gender equality and combating sexual harassment and assault against women. The movement began in 2017 as a social media campaign, with women sharing their experiences of sexual harassment and assault using the hashtag #MeToo. Since then, the movement has grown to become a global phenomenon, with millions of people sharing their stories and demanding change.
The MeToo movement has been instrumental in raising awareness about the prevalence of sexual harassment and assault against women. According to a survey by the Angus Reid Institute, 67% of Canadian women have experienced some form of sexual harassment in their lifetime.
The movement has also led to changes in how these issues are addressed in the workplace and in society more broadly. For example, many companies have introduced new policies and procedures for addressing sexual harassment and have committed to promoting greater gender equality in the workplace.
Overall, the MeToo movement has played a critical role in advancing the cause of gender equality and promoting greater awareness and understanding of the challenges faced by women in society. However, there is still much work to be done to ensure that women are able to fully participate in all areas of society, free from discrimination & harassment.
4. Solution To Inequality

In order to combat the social and workplace issues faced by women, it is important to develop potential solutions that can help promote gender equality and improve their lives. Here are some suggestions:
- Promote diversity and inclusion in the workplace by implementing hiring practices that prioritize underrepresented groups and creating a safe and welcoming work environment.
- Support victims of gender-based violence and discrimination by establishing employee resource groups, offering counseling services, and implementing zero-tolerance policies.
- Encourage women to take on leadership roles by offering mentorship programs, training, and professional development opportunities.
- Implement family-friendly policies such as flexible work hours, paid parental leave, and affordable childcare to help women balance work and family responsibilities.
- Educate both women and men about gender-based discrimination and harassment in the workplace and society as a whole to increase awareness and reduce stigma.
- Increase representation of women in politics and leadership roles by implementing quotas, promoting female candidates, and supporting organizations that advocate for gender equality.
- By implementing these solutions, we can create a more equitable and inclusive society for women.
Many countries and states worldwide are actively working to address issues related to gender equality in the workplace and society. Some notable examples include:
- Norway: known for its gender quota law, which requires that publicly traded companies have at least 40% female representation on their boards of directors
- Iceland: has been ranked the world's most gender-equal country for over a decade by the World Economic Forum, and recently passed a law requiring companies to prove they are paying men and women equally
- California, USA: has implemented various gender-related policies, such as making it necessary that publicly traded companies must have at least one woman on their board of directors by the end of 2021
- New Zealand: passed the Equal Pay Amendment Act in 2020, which aims to close the gender pay gap by ensuring that women are paid the same as men for work of equal value
These are just a few examples of the many countries and states worldwide that are taking steps towards gender equality in the workplace and society.
5. Laws for Gender Equality

Despite the ongoing challenges faced by women, there have been significant advances in legal protections for gender equality in Canada and the United States. Some of the key laws in place to promote gender equality include the Canadian Human Rights Act, the Ontario Human Rights Code, and the U.S. Title VII of the Civil Rights Act.
The Canadian Human Rights Act prohibits discrimination on the basis of gender in the workplace and other areas of society. Similarly, the Ontario Human Rights Code provides protections against gender-based discrimination in the workplace, housing, and other areas of public life. Title VII of the Civil Rights Act also prohibits employment discrimination on the basis of gender and includes provisions to address sexual harassment and pregnancy discrimination.
These laws are intended to protect women's rights and promote gender equality in the workplace and in society more broadly. By providing legal remedies for instances of gender-based harassment or discrimination, these laws help to ensure that women are able to participate fully in all areas of society, free from discrimination and bias.
However, despite the existence of these laws, more work is needed to ensure that they are fully enforced and that women are able to access their legal protections.
Click here to learn more about the Canadian Human Rights Act.
Click here to learn more about the Ontario Human Rights Code, and click here for an annotated version of the Human Rights Code.
Click here to learn more about the U.S. Title VII of the Civil Rights Act and other relevant status in the United States.
Click here to contact HTW Law - Employment Lawyer for assistance and legal consultation.

6. Ontario's Legal Answers to Gender Inequality

If we talk specifically about Ontario, Canada, it has a number of legal protections in place to promote gender equality in the workplace and society.

The Ontario Human Rights Code provides important legal safeguards for women and prohibits workplace discrimination and workplace harassment on the basis of gender identity, gender expression, and sexual orientation. This means that employers cannot discriminate against women in hiring, promotion, or pay, and cannot create a work environment that is hostile or unwelcoming to women.
Click here to learn more about legal protections against workplace harassment and workplace discrimination under the Human Rights Code.

In addition, the province has a Pay Equity Act that requires employers to pay employees of different genders equally for work of equal value. An amendment was added to the Ontario Employment Standards Act relating to equal pay for equal works. These helps to address the persistent wage gap between men and women.
Click here to learn more about the Pay Equity Act.
Click here to learn more about the equal pay for equal works under the ESA.
Pay equity act requires equal pay for equal value for men and women. Equal pay under ESA require equal pay for different workers in different locations for same skill, same level, despite different location, whether full time or part time workers.
Both legislation allows for exceptions for measurable distinction such as merit basis, seniority based, but NOT gender, religious or ethnic based. A violation of the pay equity and equal pay for equal work itself is prima facie evidence of discrimination based on gender.
Click here to learn more about the difference between Pay Equity Act and Equal Pay for Equal Works under the ESA.
These legal protections are important because they help create a more equitable society. They provide women with the tools to challenge discriminatory practices and hold employers accountable for promoting gender equality. However, it is important to note that legal protections alone are not enough to achieve gender equality. It also requires changes in societal attitudes and norms and proactive efforts by employers to promote diversity and inclusion in the workplace. A clear example is a case of midwives who demanded to pay equally.

In Association of Ontario Midwives v Ontario (Health and Long-Term Care), 2020 HRTO 165, the Human Rights Tribunal of Ontario (HRTO) ruled in favor of the Association of Ontario Midwives (AOM), finding that the Ministry of Health (MOH) unlawfully underpaid midwives due to gender discrimination, and ordering the MOH to (i) implement a 20% wage adjustment for eligible midwives retroactive to April 1, 2011, and (ii) pay $7,500.00 in damages to each eligible midwife for injury to dignity, feelings, and self-respect.
The HRTO reasoned that the midwives were almost entirely women and members of a protected group under the Code; they faced discrimination beginning in 2005, when the MOH abandoned the 1993 Principles; and, for a variety of reasons, gender was a factor in the discrimination the midwives faced and the compensation gap that developed between them and the CHC physicians since 2005.
MOH appealed the decision.

In Ontario (Health) v. Association of Ontario Midwives, 2022 ONCA 458, the Court of Appeal for Ontario (OCA) was satisfied with the reasonableness of the Human Rights Tribunal of Ontario's (HRTO) finding that the Ministry of Health (MOH) subjected midwives to pay discrimination on the basis of gender, and upheld the HRTO decision made in 2020.
The OCA found that the HRTO articulated the well-established three-step test established in Moore v. British Columbia (Education), 2012 SCC 61, to demonstrate a prima facie case of gender discrimination, namely, a claimant must show that they are a member of a group protected by the Code; they have been subjected to adverse treatment; and their gender was a factor in the adverse treatment.
The OCA concluded that the HRTO’s reasons, read holistically, revealed “a logical chain of analysis grounded in the record and the relevant jurisprudence” in support of its conclusion of discrimination.
Click here for a details in-depth explanation and analysis of Association of Ontario Midwives v Ontario (Health and Long-Term Care), 2020 HRTO 165.
Click here for a details in-depth explanation and analysis of Ontario (Health) v. Association of Ontario Midwives, 2022 ONCA 458.
Click here to read about Closing the gap: Understanding Ontario midwives’ legal action from the Association of Ontario Midwives (AOM) website.
7. While Summing Up…
In conclusion, gender equality remains a pressing issue in the workplace and society. Social and workplace issues faced by women, such as unequal pay, lack of representation in politics and leadership roles, gender-based violence and harassment, occupational segregation, and discrimination and harassment, continue to persist.
However, there are potential solutions to these issues, such as promoting diversity and inclusion, providing support for victims of gender-based violence and discrimination, and encouraging women to take on leadership roles. It is important to continue working towards gender equality in all areas of society to create a more equitable and just world for all.
You don't have to fight the battle alone. Speaking with an employment lawyer who is familiar with the laws and regulations regarding workplace harassment and workplace discrimination, and gender inequality against women will go a long way. If you are in doubt, it's essential that you reach out for help as soon as possible right away.
Click here to contact HTW Law - Employment Lawyer for assistance and legal consultation.


Author Bio:
Melissa Calvert is currently working as assistant researcher at crowdwriter.com. She was previously associated with a reputed firm as an SEO Analyst. Melissa likes to travel, and she often travels solo to explore different cultures of various places. In her leisure time, you will find her reading books and browsing technological advancements.

Sources:
- https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/89-503-x/2015001/article/14694-eng.htm
- https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/85-002-x/2019001/article/00018-eng.htm
- https://angusreid.org/story-10-the-metoo-movement/
- https://www.elections.ca/content.aspx?section=res&dir=rep/off/sta_2019&document=index&lang=e
- https://www.eeoc.gov/types-discrimination
- https://psycnet.apa.org/doiLanding?doi=10.1037%2F0021-9010.82.4.578
- https://www.jstor.org/stable/2657415?origin=crossref
- https://www.unwomen.org/en/what-we-do/ending-violence-against-women/facts-and-figures
Article Source : www.htwlaw.ca/post/gender-e...